Durometer
Simplicity and Performance
Our hardness testers are designed to meet the most demanding requirements for precision and reliability.
Discover our durometer range
Digital model
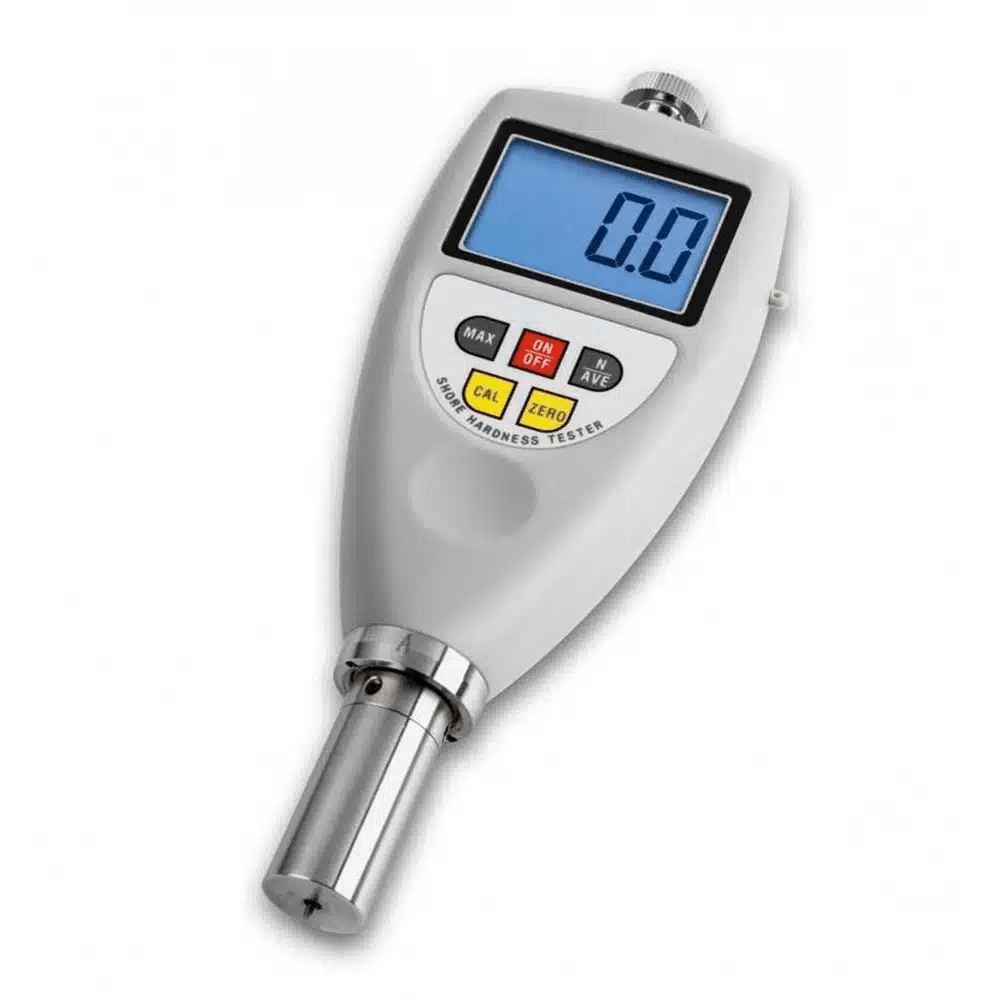

Held in place by a spring, a metal tip of defined shape is pressed against the sample. The depth of the impression can then be used to determine the hardness or softness of the material.
This procedure is described in DIN ISO 7619-1:2012.
Analog model
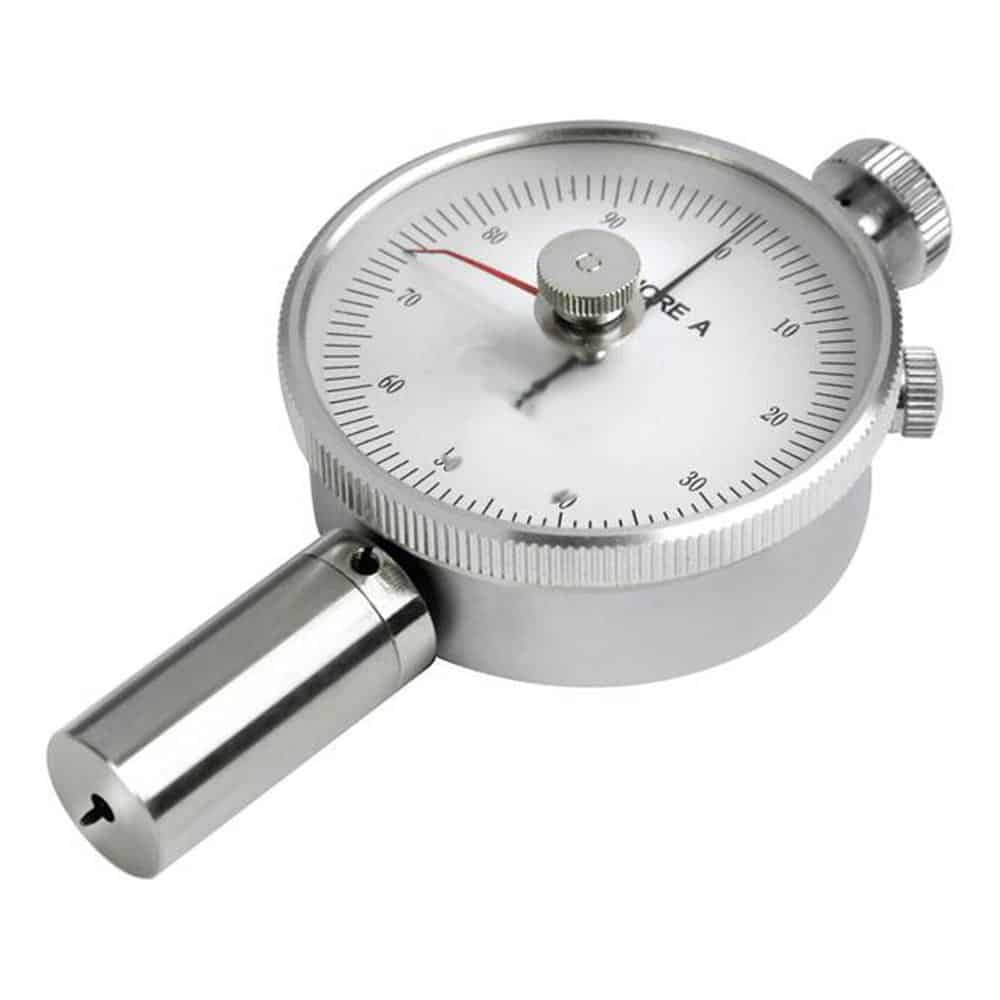

This hardness tester makes measuring the hardness of plastics simple and straightforward.
Held in place by a spring, a metal tip of defined shape is pressed against the sample. The depth of the impression can then be used to determine the hardness or softness of the material.
This procedure is described in DIN ISO 7619-1:2012.
Premium model
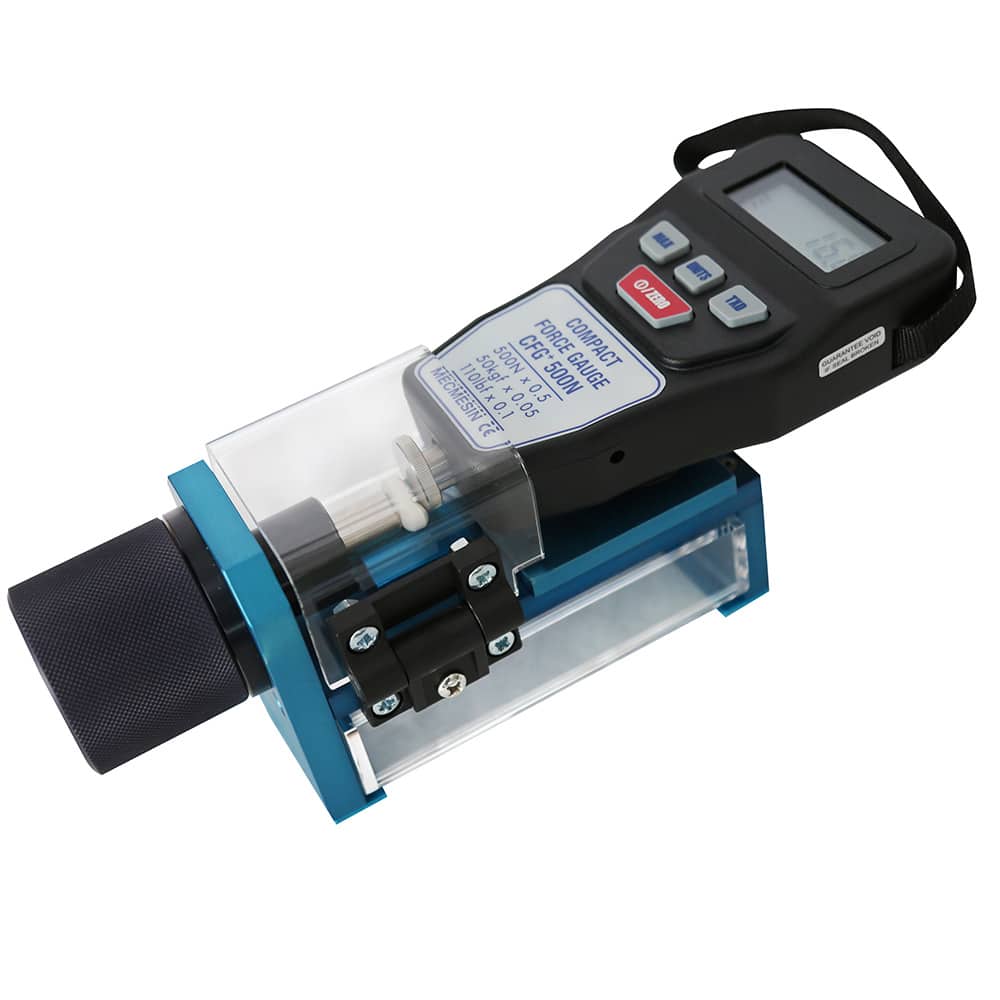

Portable tablet and pill hardness tester
The DCX system allows the precise and completely autonomous measurement of tablet hardness by applying a compressive force. The breaking load is read on a calibrated force gauge.
A protective cover prevents accidental splashing on the operator.
The reading is taken digitally, on the 200 N or 500 N dynamometer depending on the type of equipment chosen.
Options and accessories

EU charger
Mains charger compatible with European plugs (type C/F – 230V). Ideal for use in all European Union countries. Complies with current safety standards.

US charger
Mains charger compatible with American plugs (type A/B – 120V). Designed for use in the USA, Canada and countries using this standard. Complies with local safety standards.
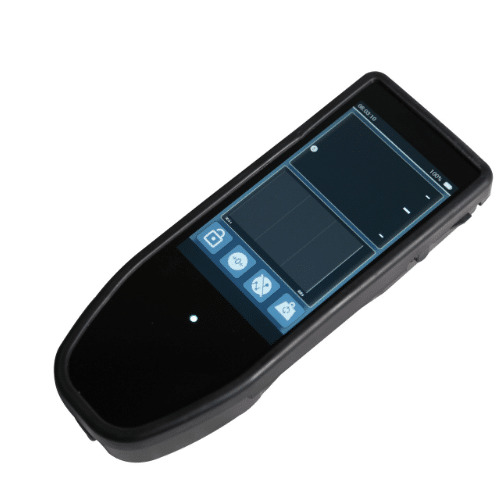

Other force gauges on request
The durometer can be adapted to other dynamometers to meet your specific requirements. Please contact us to find the right model for your application.
Other tablet sizes on request
The device can be adapted to other tablet sizes according to your requirements. Please contact us for a customized configuration.
Frequently asked questions about durometer
What is a durometer?
A durometer is a device that measures the hardness of a material. It is often used to test materials such as rubber, plastic, wood and metals.
What are the different Shore hardness scales?
There are two main Shore hardness scales:
Shore A : for soft materials such as rubber
Shore D : for harder materials such as rigid plastics.
These scales can be used to determine the hardness or softness of a material.
How does a durometer work?
The hardness tester uses a steel tip with a specific shape and size to exert pressure on the surface of the material to be tested. The penetration depth of the tip is measured and converted into a hardness value, usually expressed in Shore units.
Why use a durometer test stand?
Using a test bench with a durometer enables more accurate and consistent measurements. This combination ensures greater stability and repeatability in hardness testing.
In what industry is the durometer used?
Hardness testers are used in many industries where the measurement of material hardness is essential. Here are a few areas of application :
-
Automotive Industries
- Hardness testing of tires, rubber seals, plastic and metal parts to ensure durability and compliance with standards.
-
Aeronautics & aerospace
- Checking the hardness of coatings, composite components and metal parts to ensure aircraft safety and performance.
-
Plastics and rubber industry
- Hardness testing of polymers and elastomers to ensure they meet specific application requirements.
-
Construction and Public Works Sector
- Measures the hardness of materials such as concrete, coatings and industrial flooring.
-
Medical & biomaterials
- Hardness testing of medical implants, prostheses and equipment made of rubber or plastic used in the medical field.
-
Electronics & component manufacturing
- Checking the hardness of silicone components, plastics and encapsulating materials.
Contact us
Need advice or a personalized quote?
At ACRN, we know that every hardness measurement requirement is unique. That’s why our hardness testers, whether new or compatible with your existing equipment, are designed to guarantee precision, reliability and performance.
✅ Why choose our durometers?
-
Optimum precision for reliable, reproducible measurement results.
-
Customized options to suit your specific materials and requirements.
-
Technical support from measurement specialists.
Fill in the form opposite to :
-
Ask your questions.
-
Ask for a quote.
-
Get expert advice.
📞 An urgent request?
Call us direct on 02 32 80 81 40 or write to us at contact@acrn.fr.
Our team is here to help you make your projects a reality!
